The introduction of DBMS initiates a new era for dry Bulk operators; it reminds us the times back when TMSA entered the liquid cargo sector. Thus, it is interesting to draw parallels and find key differences into these two milestone tools which aim to drive excellence in the maritime industry.
In particular, TMSA is a safety tool for liquid cargo ship owners; a self-audit and assessment tool, based on businesses best practices from oil majors. The KPIs used have been answered with a ‘Yes or No’ as it is important to clarify compliance or not compliance. For every positive answer, operators have to fully justify results and therefore they need to have in place documented systems and procedures and provide evidence that these systems / procedures are effectively implemented both onboard and ashore.
Following the example, the dry sector now has something quite similar, considering that DBMS is seen as a self assessment tool that can determine current status of operator and Level of compliance.
TMSA and DBMS: Similarities and Differences
Stages vs Levels
As already mentioned, both tools are based on self assessment processes. It is voluntary for ship owners to declare the compliance level and status of the managed company. Operator has to review a list of KPIs (or expectations) and decide the compliance (or not) for each one. There are four (4) compliance levels in both standards.
| TMSA | DBMS |
| Stage 1 | Basic |
| Stage 2 | Intermediate |
| Stage 3 | Advanced |
| Stage 4 | Excellence |
Although separation is not clear between levels, there seems to be a relation between the levels of these two requirements. Basically both aim to ensure a level of compliance (Stage 1 / Basic) on ISM requirements and then move to continuous improvement based on measurable KPI’s (stage 2&3/Intermediate & Advance). Moreover, Stage 4 and Excellence are levels which show that high proactive compliance exists.
KPIs vs Expectations
TMSA uses several Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and Best Practices while DBMS uses Expectations that set Targets, suggesting Objective evidence for each. There is no ranking in DBMS but phrases are being used eg Subject Area 1, Level Basic, Expectation xxxxxx, Target yyyyyy; this could be one of the comments for evaluation now that the Standard is in draft since numbers work best at such occasions. (Eg KPI 1.1.1)
Elements vs Subject Areas
On the other hand, TMSA includes 13 elements while DBMS has 30 subject areas. Taking into consideration the requirements of each one, table below shows a relation. However, there is no clear matching between TSMA elements and DBMS Subject areas since KPIs and targets accordingly can be included in different sections. Nonetheless, the generic approach is same and all related items are covered in both standards.
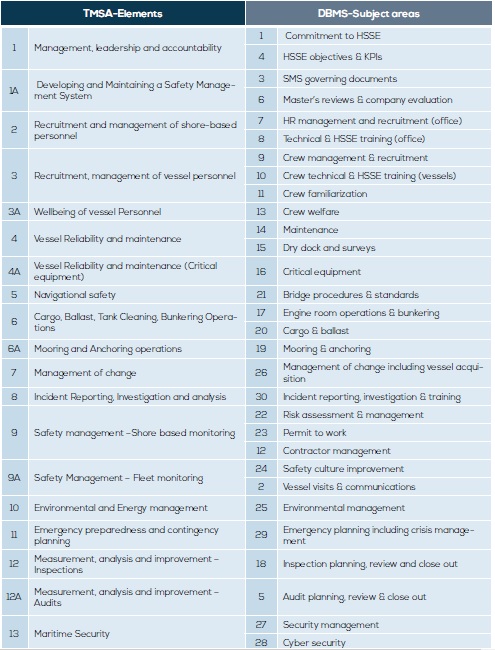
What’s more, DBMS seems to be more analytic; each item is divided into several areas in order to be more comprehensive to the operator.
The scoring processes
Scoring is included in both standards with more or less similar approach. Percentage (%) compliance of KPIs/Targets is divided with total items in order to have a number (1, 2.75 etc) instead of percentage.
In TMSA, operator cannot move to next Stage unless the previous is fully implemented. In DBMS, operator can move to next level of compliance but with reduced scoring if the previous levels are not 100% completed.
In this regard, a key issue to be considered for DBMS would be how the % compliance should be satisfactory for the next level. In addition to this, not having separate targets (or expectations), as per in TMSA where KPIs are numbered, it makes it difficult to understand the compliance of each in relation with the required objective evidence.
For TMSA all elements have the same importance, and there is no difference to scoring. DBMS, in its guidance notes, declares that there is no gravity Subject areas and all have the same importance for scoring. However in the same section there are seventeen (17) subject areas considered as Priority Areas. These cover the 4 pillars of Standard base (Performance, People, Plant, Process).
Lastly, another difference that exists between TMSA and DBMS, is that while TMSA also covers inland shipping, DBMS is focused on vessels carrying dry cargo in bulk at sea.
Source: Safety4Sea
